How To Justify Building Repairs
Abstruse
We spend nigh of our time within buildings, only did you know that owning a building can be very expensive? There are many tasks we need to practice on a regular basis to keep our buildings in good shape. These tasks are called maintenance, and they require materials and labor, which cost money. Therefore, building owners attempt to keep their buildings in proficient shape for as long as possible. Buildings can also take negative impacts on the surroundings, which we want to avoid. Past analyzing how a building'due south condition changes over its lifetime, we can predict when it will need maintenance. This allows us to fix problems before they go more expensive and worse on the environment. To practice that, engineers apply a procedure called life-cycle analysis to make decisions on where and when to invest time and coin on building maintenance. In this article, we will explain life-cycle analysis and use the example of a house to describe the concept.
What Do We Demand to Know to Keep Buildings Healthy?
Buildings, such as your business firm, consist of many parts. These parts are called components , and each one serves a purpose. The components of a house include the foundation, roof, gutters, windows, siding, electrical organisation, plumbing, walls, and more. All of the components must piece of work together to fulfill the building's purpose [1]. If one of the components fails, the entire building may not be very useful. Imagine a storm suddenly blows a tree over, and it pokes a pigsty in the roof of your business firm. The residuum of the house's components, like the plumbing, might work fine. Only the roof failure means that the building fails its purpose, which is to proceed yous warm and dry.
Buildings, like your house, cost money to build or purchase, but on top of this initial toll, there are ongoing maintenance and repair costs. The maintenance and repair costs include many tasks that require both time and money. For example, as shown in Figure one, a house needs a new roof every 20 years; the gutters need to be cleaned every fall; the air-conditioning parts demand to be cleaned every few months; holes in the siding need to be repaired frequently; the bathrooms need to be renovated every 20 years; your sister's room needs to be repainted when her favorite color changes; and more. The number of tasks over your house's long lifetime, known as its life bike, really add together up. This is what makes the maintenance phase then expensive. Nevertheless, we invest time and money into our houses considering maintenance helps brand their life cycles longer.
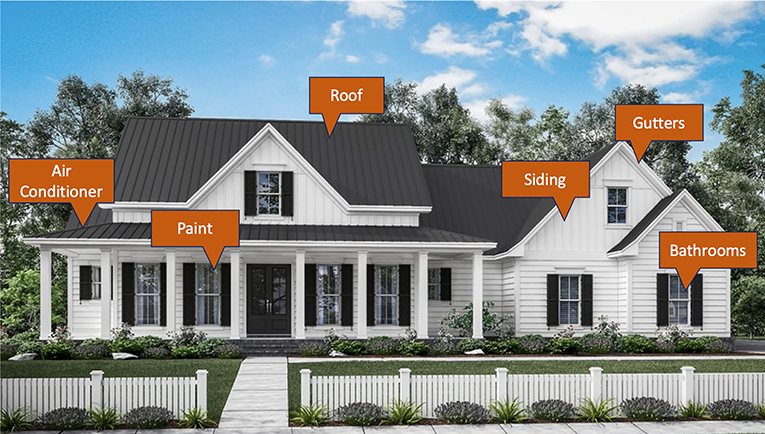
- Figure 1 - Components of a business firm that volition demand repair include the roof, air conditioner, siding, and more.
- Each of these components may fail after a different amount of time.
In improver to costing money, each building also has an impact on the surroundings around information technology. These impacts are ofttimes negative [two]. For example, the country your house was congenital on was cleared of plants and trees. Removing plants forces the animals that lived there to move, which is bad for the environment. The woods used to construct the walls was collected with equipment that runs on fossil fuels and pollutes the air. When the roof gets replaced, the old fabric is taken to a landfill. And if we practise not take care of the air workout arrangement properly, the fluids needed to run it can be harmful to the air we breathe.
Allow usa think even bigger than a single component. As you may imagine, larger buildings, like factories, require more maintenance than your firm because they have more components. If a factory has five air conditioning units instead of 1, how can the owners possibly track when each air workout unit needs to be replaced? The components that brand up a building cannot last forever. All equipment and materials pause down over time. Eventually, some component will be in such bad condition that it must be repaired or replaced. However, each component has its own, unique life cycle. The air conditioning parts may last 6 or 7 years, but the building's roof might last 20 years. Building owners collect data on each component to see how long it usually lasts. Collecting data is the start footstep in performing a life-bike assay , which helps keep maintenance and repair tasks organized.
Why Maintain Buildings With Life-Cycle Analysis?
Life-bike analysis is a methodical and scientific tool used to analyze a edifice throughout its lifetime, in lodge to brand decisions regarding maintenance and repair [3, 4]. This definition sounds complicated, merely we will pause it down. "Methodical" means that the life-wheel analysis follows a clear set of steps that we tin repeat over and over. Being methodical is near important for big buildings with many components. "Scientific" means that the process is backed by information and research. Engineers accept developed multiple ways to predict how long a edifice will last and how much it will impact the environment. Math equations make this possible. The phrase "throughout its lifetime" ways we collect information on the condition of the building at multiple times. Nosotros desire to larn about the building'southward status at the start of its life, the end of its life, and every point in between. We cannot predict the verbal fourth dimension that a building will demand maintenance, because that depends on many factors. These factors include weather, how much the building is used, and how much maintenance we do [1]. However, by analyzing a lot of data, we tin make reasonable predictions. Finally, "brand decisions" refers to why nosotros chose to behave a life-cycle analysis. Typically, we utilize data to brand decisions on how to spend our coin. Nosotros want to know when to repair each component. Again, repairs can help buildings last longer and decrease their impact on the environs. Repairs are plush, however, and building owners also want to minimize their costs.
Figure 2A shows when a building component, similar the roof, would normally fail if no maintenance or repair work was washed. The roof goes from expert status to boilerplate condition to bad status over time. However, through proper life-cycle analysis, engineers tin gauge when components are most likely to fail. In Figure 2A, we show a roof declining after a few years. Nosotros made this prediction based on feel with many buildings, and nigh of those roofs failed around the same time. With this knowledge, we tin plan maintenance and repair projects before the roof caves in completely. The most efficient fourth dimension to invest in repairs is before failure [i]. Because we know when the roof is likely to fail, Figure 2B shows a repair being completed before that failure fourth dimension. The repair improves the building'due south condition right away. Afterwards the repair, the roof all the same goes from expert condition to boilerplate condition to bad condition. Nonetheless, this happens at a afterwards fourth dimension than in Figure 2A. Each maintenance or repair chore can increase the building'southward life by a few months or even years. In the stop, the roof's life wheel has been increased. Additionally, certain maintenance tasks can besides reduce the building'due south environmental touch on. For example, we can trade out old, incandescent low-cal bulbs for more efficient, globe-friendly lite-emitting diodes (LEDs). This task will decrease the amount of free energy needed to light the building. This is both cost-effective and better for the environment.
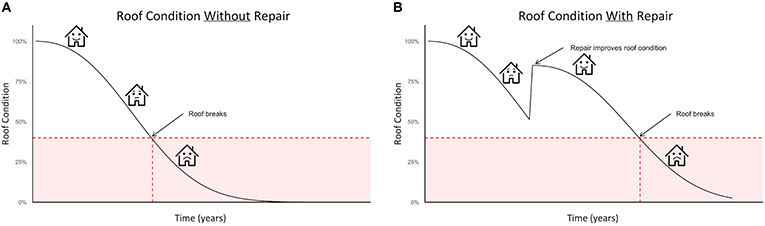
- Figure 2 - (A) If no repairs are completed, a firm will eventually fail.
- (B) Withal, if repairs are done before failure, the house will final longer. Maintenance and repairs can increase the house'south life, and some repairs tin reduce the house's cost and environmental affect.
Let us consider your firm once again. Your parents may clean the gutters every fall, to remove the leaves and branches that collect. They could clean the gutters every calendar week, only that would take a lot of time. What if your parents waited and only cleaned up once every 5 years? Then the gutters could get chock-full and your roof might commencement to leak. A leaky roof is much more expensive to set up than cleaning the gutters. Plus, fixing the roof would crave you to dispose of shingles, wood, and nails, which is bad for the environs. This example shows that there is a best time to invest in maintenance and repair projects. Doing tasks too early is wasteful. But, doing tasks also late can permit small issues to grow into larger, more expensive bug. Analyzing data from a edifice can help usa estimate when components will fail. We also know that the best time to consummate a repair is just before the failure betoken. This allows us to optimize the building's functioning and environmental impact at the lowest price possible.
Decision
Building life-cycle assay is a concept nosotros use to take care of our buildings. We analyze the building's condition throughout its life in gild to selection the best fourth dimension to invest in repair and maintenance tasks. Investing at the correct time helps the building last longer and minimize its impact on the environment. This is unproblematic for one component, but information technology can get complicated rapidly. Buildings have hundreds of components, and each 1 has a different life expectancy. The life-bicycle analysis process provides articulate steps to follow. By following these steps, owners can decide on the all-time time to invest in their building.
Glossary
Component: ↑ A part that makes up a whole when combined with other parts.
Maintenance: ↑ The tasks that must be washed to continue belongings or equipment in good shape.
Life-wheel Analysis: ↑ A way to wait at the costs and environmental impacts of repair on a edifice throughout its entire life.
Analysis: ↑ A detailed study of something complex in lodge to understand how it works.
Methodical: ↑ Following a articulate ready of steps that can exist repeated over and over.
Author Contributions
JF, SS, and AH contributed the conception and design of the paper. JF wrote the first draft of the manuscript. SS and AH revised the sections of the manuscript. AH provided the content expertise. All authors contributed to the manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the enquiry was conducted in the absenteeism of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
[1] ↑ Grussing, G. Due north., and Marrano, L. R. 2007. "Edifice component lifecycle repair/replacement model for institutional facility management," in Proceedings of the 2007 International Workshop on Computing in Ceremonious Engineering, eds Fifty. Soibelman and B. Akinci (Pittsburgh, PA: American Gild of Civil Engineers). p. 550-57. doi: 10.1061/40937(261)65
[2] ↑ Medineckiene, G., Turskis, Z., and Zavadskas, Eastward. K. 2022. Sustainable structure taking into account the building impact on the environs. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 18:118–27. doi: 10.3846/jeelm.2010.14
[3] ↑ ISO 14040. 2006. Environmental Management–Life Cycle Assessment–Principles and Framework. ISO 14040. International Organization for Standardization. Available online at: https://world wide web.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:14040:ed-2:v1:en
[4] ↑ Bayer, C., Gamble, Thou., Gentry, R., and Joshi, S. 2022. AIA Guide to Building Life Wheel Assessment in Practise. Washington, DC: The American Establish of Architects
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/479397
Posted by: robertabilootich1963.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Justify Building Repairs"
Post a Comment